PEMDAS 1.01 released January 11, 2007. Several bugs came to my attention within the past couple days that I thought were important enough to fix in a minor update, so. Also remember that we always have to do the multiplication or division first with our points, and then the adding and subtracting (sort of like PEMDAS). Here is the t-chart with the original function, and then the transformations on the outsides. Now we can graph the outside points (points that aren’t crossed out) to get the graph of the. Get your assignment help services from professionals. Cheap essay writing sercice. If you need professional help with completing any kind of homework, Online Essay Help is the right place to get it. Jul 08, 2018 The following are some of the multiple questions from the recent June 2018 New York State Common Core Geometry Regents exam. June 2018 Geometry, Part I. BlueWater 50 bulan yang lalu PEMDAS adalah urutan operasi matematika, yaitu: 1. Tanda kurung ('P'arentheses) 2. Pangkat dan akar ('E'xponents) 3. Perkalian dan pembagian ('M'ultiplication, 'D'i.
Welcome! PEMDAS was created to remember the math order of operations. Here we will explain the order of operations, explain why the order of operations is important, and showyou how you can use PEMDAS to remember the order of operations.In addition to that, we also have a PEMDAS Calculator and PEMDAS examples and practice problems. Our goal is to make you a PEMDAS expert.
Math Operations
Math operations are binary operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. You useoperations to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and so on.
Math Order of Operations
If you are doing more than one operation, you must do them in the correct order to get the correct answer. Here is themath order of operations:
1 - Parentheses
2 - Exponents and Roots
 3 - Multiplication
3 - Multiplication4 - Division
5 - Addition
6 - Subtraction
Why is the Order of Operations Important?
The math order of operations is important because it will ensure you get the correct answer. Here is anexample to illustrate two ways to calculate 1 + 2 × 3
Incorrect: 1 plus 2 equals 3, and then 3 times 3 equals 9.
Correct: 2 times 3 equals 6, and then 6 plus 1 equals 7.
The example above illustrates that you must do the calculations in the correct order of operations to get the correct answer. You cannot simply calculate from left to right and get the correct answer in all instances.
PEMDAS Rule
So what does PEMDAS mean? PEMDAS is an acronym. PEMDAS is an easy way to remember the math order of operations. If you look at the list of operations above, yousee that the first letter of each operation in order spells PEMDAS. Here is the order of operations with the corresponding letter to spell PEMDAS:
P - Parentheses
E - Exponents and Roots
M - Multiplication
D - Division
A - Addition
S - Subtraction
PEMDAS Calculator
The PEMDAS Calculator below allows you to enter different numbers with different operations. We willthen use PEMDAS to make sure to calculate the problem in the correct order to get the correct answer.
How to Remember PEMDAS
To remember the term PEMDAS, people have made sentences from the letters. Examples of sentences include 'Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally' and 'Popcorn Every Monday Donuts Always Sunday'. Some argue that the operationsin PEMDAS become easier and easier. Thus, you just do the parentheses first, then less and less difficult operations.
PEMDAS Summary
PEMDAS does not really have a meaning. PEMDAS is the first letter of each math order of operation: First you solve what is inside parentheses, then you calculateexponents and roots, then you multiply, followed by dividing, then adding, and finally subtraction.
PEMDAS Examples
Below are some examples of PEMDAS problems to practice. Use the skills you learned on this page to find the answer and then check the solution.
3 + 4 ÷ 2 - 4 = Answer
4 ÷ 2 ^ 2 - 4 = Answer

1 + 2 - 3 × 3 + 4 ^ 2 = Answer
1 - 2 × 3 × 4 = Answer
7 - 1 × 0 + 3 ÷ 3 = Answer
PEMDAS Rank and Priority
Multiplication and Division (MD in PEMDAS) have equal rank in the order of operations and do not need to be in order.Addition and Subtraction (AS in PEMDAS) also have equal rank and do not need to be in order. You could, for example, subtract before you add.The reason they have equal rank or priority is because the operations are inverse or are compliments of each other. Thus, the order of operations could also be interpreted as follows:
1 - Parentheses
2 - Exponents & Roots
3 - Multiplication & Division
5 - Addition & Subtraction
PEMDAS Around the World
Math is math and the order of operations is the same all over the world. However, the operations may be called different things.For example, in Great Britain PEMDAS is called BODMAS because they call their operations Brackets, Orders, Divisions, Multiplications,Additions, and Subtractions. Furthermore, in Canada they also call parentheses brackets and their version of PEMDAS is BEDMAS.
What is the Order of Operations?
The phrase “order of operations” or “PEMDAS” refers to the order in which you need to perform multiplication, division, addition, subtraction, and exponential operations in an equation.

To see the free study questions, please go to the next section.
Order of Operations – PEMDAS
The phrase PEMDAS is sometimes used to remember the correct order to perform operations in an equation.
PEMDAS means parentheses, exponents, division, multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
So, when you see an equation, you need to perform the operations from left to right in this order:
1) Parentheses – Do the operations inside parentheses or brackets first.
2) Exponents – Then perform the operations indicated by the exponents.
3) Multiplication and Division – Then do the multiplication and division from left to right.
4) Addition and Subtraction – Then do the addition and subtraction from left to right.
Some students remember the rule “PEMDAS” by using the phrase:
PEMDAS: Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally
Pemdas With Parentheses
Let’s look at a couple of problems on PEMDAS or order of operations.
Order of Operations PEMDAS – Basic Example
Now study this example of how to carry out the order of operations “PEMDAS” rule.
Example: 1 + 64 ÷ 4 ÷ 2 × 5 – 3 = ?
Answer: 38
In this problem, we do not have any parentheses or exponents to deal with.
So, start by doing the multiplication and division first.
Multiplication and division are performed in the same step, so you need to divide and then multiply from left to right as shown below when you have division and multiplication together like in this example.
Pemdas With Division
1 + 64 ÷ 4 ÷ 2 × 5 – 3 =
1 + (64 ÷ 4) ÷ 2 × 5 – 3 =
1 + 16 ÷ 2 × 5 – 3 =
1 + (16 ÷ 2) × 5 – 3 =
1 + 8 × 5 – 3 =
1 + (8 × 5) – 3 =
1 + 40 – 3
Then do the addition and subtraction from left to right.
1 + 40 – 3 =
41 – 3 = 38
Order of Operations PEMDAS – Advanced Example
Let’s look at a more difficult example of how to carry out the order of operations “PEMDAS” rule.
Example: (4 + 5)2 + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6 = ?
Answer: 72
Do the operations in the parentheses first.
(4 + 5)2 + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6 =
(9)2 + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6
Then do the exponential operation. Office for mac serializer.
92 + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6 =
(9 × 9) + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6 =
81 + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6
Next do the multiplication and division from left to right.
81 + 9 ÷ 3 – 2 × 6 =
81 + (9 ÷ 3) – 2 × 6 =
81 + 3 – 2 × 6 =
81 + 3 – (2 × 6) =
81 + 3 – 12
Then do the addition and subtraction from left to right.
81 + 3 – 12 =
(81 + 3) – 12 =
84 – 12 = 72
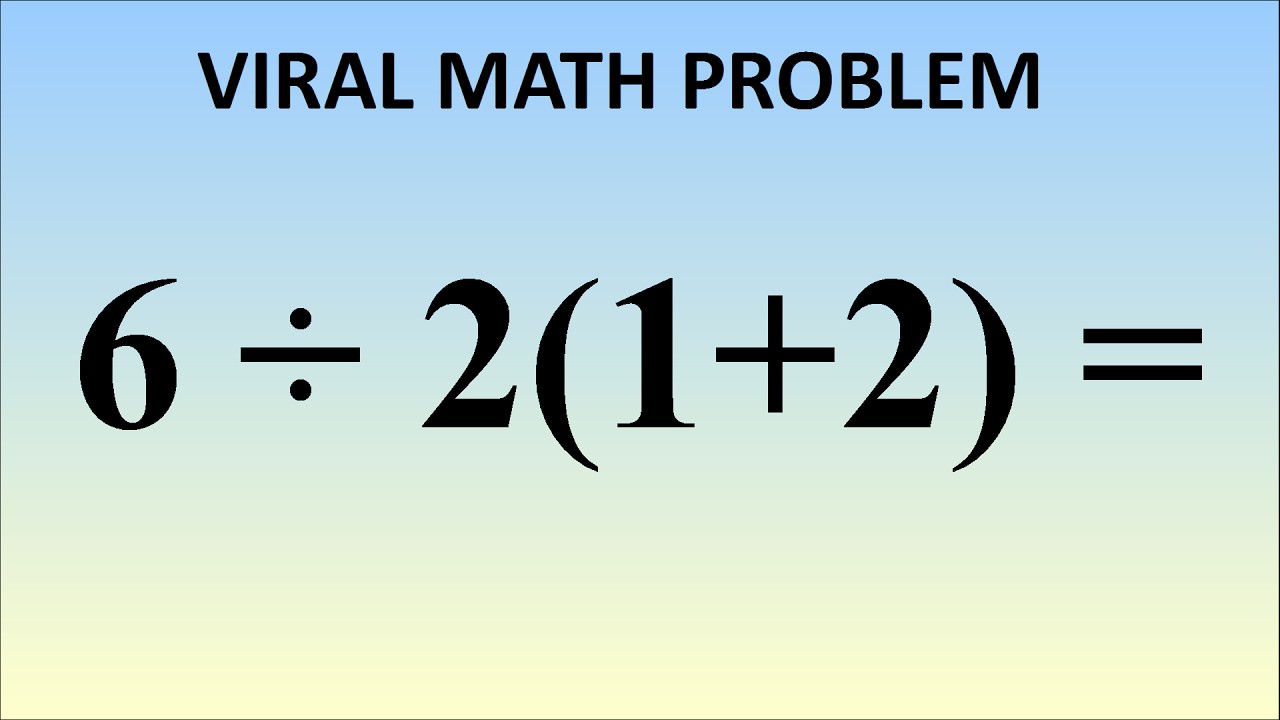
Order of Operations PEMDAS – Further Practice
If you found these exercises difficult, you should try our pre-algebra problems.
If you are testing in college math, you may also want to look at our other algebra study materials.
